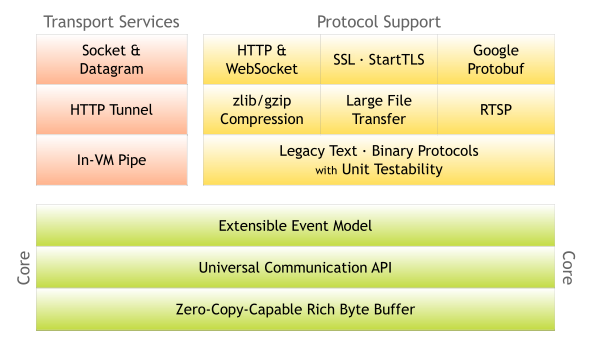
概述
原生NIO存在的问题
NIO的类库和API繁杂,使用麻烦
需要具备其它的额外技能如Java多线程编程、网络编程等
开发工作量和难度都非常大,如客户端面临断连重连、网络闪断、半包读写、失败缓存、网络拥塞和异常流的处理等。
JDK NIO存在一些Bug
Netty
Netty是由JBOSS提供的一个Java开源框架。Netty提供异步的、基于事件驱动的网络应用程序框架,用以快速开发高性能、高可靠性的网络IO程序
Netty可以帮助我们快速、简单的开发出一个网络应用,相当于简化和流程化了NIO的开发过程
Netty是目前最流行的NIO框架,Netty在互联网领域、大数据分布式计算领域、游戏行业、通信行业等获得了广泛的应用。知名的Elasticsearch、Dubbo框架内部都采用了Netty
Netty的优点
设计优雅:适用于各种传输类型的统一API阻塞和非阻塞Socket;基于灵活且可扩展的事件模型,可以清晰地分离关注点;高度可定制的线程模型-单线程,一个或多个线程池
使用方便:详细记录了Javadoc,用户指南和示例,没有其它依赖项
高性能、吞吐量更高:延迟更低,减少资源消耗,最小化不必要的内存复制
安全:完整的SSL/TLC和StartTLS支持
社区活跃、不断更新:社区活跃,版本迭代周期短,发现的bug可以被及时修复,同时,更多的新功能会被加入。
Netty高性能架构设计
线程模型
目前存在的线程模型有:
传统阻塞I/O服务模型
Reactor模式;根据Reactor的数量和处理资源池线程的数量不同,有3种典型的实现:
单Reactor单线程
单Reactor多线程
主从Reactor多线程
Netty线程模式主要就是基于主从Reactor多线程模型 做了一定的改进。
传统阻塞I/O服务模型
采用阻塞I/O模式获取输入的数据,每个连接都需要独立的线程完成数据的输入、业务处理和数据返回
存在的问题:
当并发数很大时,就会创建大量的线程,占用很多系统资源
连接创建后,如果当前线程暂时没有数据可读,该线程就会被阻塞,导致线程资源浪费
Reactor模式
Reactor模式解决传统阻塞I/O服务模型存在问题的方案:
基于I/O复用 模型:多个连接共用一个阻塞对象 ,应用程序只需要在一个阻塞对象等待,无需阻塞等待所有连接。当某个连接有新的数据可以处理时,操作系统通知应用程序,线程从阻塞状态返回,开始进行业务处理。
基于线程池复用 线程资源:不必再为每个连接创建线程,将连接完成后的业务处理任务分配给线程进行处理,一个线程可以处理多个连接的业务。
核心组成:
Reactor:Reactor在一个单独的线程中运行,负责监听和分发事件,分发给适当的处理程序来对IO事件做出反应。
Handlers:处理程序执行I/O事件要完成的实际事件。Reactor通过调度适当的处理程序来响应I/O事件,处理程序执行非阻塞操作。
单Reactor单线程
单Reactor单线程
优点:
模型简单,没有多线程、进程通信、竞争的问题,全部都在一个线程中完成
缺点:
性能问题,只有一个线程,无法完全发挥多核CPU的性能。Handler在处理某个连接上的业务时,整个进程无法处理其它连接事件,容易导致性能瓶颈
可靠性问题,线程意外终止,或进入死循环,会导致整个系统通信模块不可用,不能接收和处理外部消息,造成节点故障。
单Reactor多线程
单Reactor多线程
Reactor对象通过select监控客户端请求事件,收到事件后,通过dispatch进行分发
如果建立连接请求,则由Acceptor通过accept处理连接请求,然后创建一个Handler对象处理各种事件
如果不是连接请求,则由Reactor分发调用对应的Handler来处理
Handler只负责响应事件,不做具体业务处理,通过read读取数据后分发给后面的worker线程池的某个线程处理业务
Worker线程池会分配独立线程完成真正的业务并将结果返回给Handler
Handler收到响应后,通过send将结果返回给客户端
优点:
缺点:
多线程数据共享和访问比较复杂
reactor处理所有的事件的监听和响应,在单线程运行,在高并发场景容易出现瓶颈
主从Reactor多线程
主从Reactor多线程
Reactor主线程MainReactor对象通过select监听连接事件,收到事件后,通过Acceptor处理连接事件
当Acceptor处理连接事件后,MainReactor将连接分配给SubReactor
SubReactor将连接加入到连接队列进行监听,并创建Handler进行各种事件处理
当有新事件发生时,SubReactor就会调用对应的Handler处理
Handler通过read读取数据,分发给Worker线程池分配独立的线程进行业务处理并返回结果
Handler收到响应的结果后,再通过send将结果返回给Client
Reactor主线程可以对应多个Reactor子线程,即MainReactor可以关联多个SubReactor
优点:
缺点:
Netty模型
Netty模型
Netty抽象出两组线程池:BossGroup专门负责接收客户端的连接,WorkerGroup专门负责网络的读写
BossGroup和WorkerGroup类型都是NioEventLoopGroup
NioEventLoopGroup相当于一个事件循环组,这个组中含有多个事件循环,每个事件循环是NioEventLoopNioEventLoop表示一个不断循环地执行处理任务的线程,每个NioEventLoop都有一个Selector,用于监听绑定其上的socket的网络通讯NioEventLoopGroup可以有多个线程,即可以含有多个NioEventLoop每个Boss下的NioEventLoop循环执行的步骤:
轮询accept事件
处理accept事件,与client建立连接,生成NioSocketChannel,并将其注册到某个Worker NioEventLoop上的Selector
处理任务队列的任务,即runAllTasks
每个Worker下的NioEventLoop循环执行的步骤:
轮询read、write事件
处理I/O事件,即read、write事件,在对应的NioSocketChannel处理
处理任务队列的任务,即runAllTasks
每个Worker的NioEventLoop在处理业务时,会使用pipeline,pipeline中包含了channel,即通过pipeline可以获取到对应的channel,pipeline中维护了很多的处理器
简单案例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception System.out.println("server ctx=" + ctx); ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("客户端发送消息:" + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); System.out.println("客户端地址:" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress()); } @Override public void channelReadComplete (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello, 客户端~" , StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception ctx.close(); } } public class NettyServer public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8 ); try { ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new NettyServerHandler()); } }); System.out.println("服务器已准备好" ); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception System.out.println("client" + ctx); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello, server" , StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("服务器回复:" + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); System.out.println("服务器地址:" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress()); } @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } } public class NettyClient public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandler()); } }); System.out.println("客户端已准备好" ); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1" , 8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
几个问题:
ChannelHandlerContext、Channel和Pipeline的关系
Channel和Pipeline的关系是互相包含的关系,Channel中包含了pipeline,pipeline中也包含了channel,而ChannelHandlerContext(上下文)则是同时包含了channel和pipeline)
任务队列(TaskQueue)
三种典型使用场景:
用户程序自定义的普通任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run () try { Thread.sleep(10 * 1000 ); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("2->hello, 客户端~\n" , StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); System.out.println("OK" ); }
用户自定义定时任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override public void channelRead (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() { @Override public void run () try { Thread.sleep(5 * 1000 ); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("10s->hello, 客户端~" , StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, 5 , TimeUnit.SECONDS); System.out.println("OK" ); }
非当前Reactor线程调用Channel的各种方法
例如在推送系统 的业务线程里面,根据用户的标识 ,找到对应的Channel引用 ,然后调用Write方法向该用户推送消息,就会进入到这种场景。最终的Write会提交到任务队列后被异步消费
异步模型
异步的概念和同步相对。当一个异步过程调用发出后,不能立刻得到结果。实际处理这个调用的组件 在完成后,通过状态、通知和回调来通知调用者
Netty中的I/O操作是异步的,包含Bind、Write、Connect等操作会简单的返回一个ChannelFuture
调用者不能立即得到结果,而是通过Future-Listener机制,用户可以方便地主动获取或者通过通知机制获得IO操作结果
Netty异步模型是建立在future和callback之上的。callback就是回调。future的核心思想是:假设一个方法fun,计算过程非常耗时,等待fun返回显然不合适,则可以在调用fun的时候立即返回一个future,后续可以通过future去监控fun方法的处理过程(即:Future-Listener机制)
Future说明:
表示异步的执行结果,可以通过它提供的方法来检测执行是否完成
ChannelFuture是一个接口,可以添加监听器,当监听的事件发生时,就会通知到监听器
例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete (ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception if (channelFuture.isSuccess()) { System.out.println("监听端口8888成功" ); } } });
相比传统阻塞I/O,执行I/O操作后线程会被阻塞住,直到操作完成;异步处理的好处是不会造成线程阻塞,线程在I/O操作期间可以执行别的程序,在高并发情形下会更稳定和更高的吞吐量
Http服务端案例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class HttpServer public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8 ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new HttpServerInitializer()); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class HttpServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer <SocketChannel > @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception ch.pipeline().addLast("myHttpServerCodec" , new HttpServerCodec()) .addLast("myHttpServerHandler" , new HttpServerHandler()); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class HttpServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler <HttpObject > @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpObject msg) throws Exception if (msg instanceof HttpRequest){ System.out.println("msg 类型=" + msg.getClass()); System.out.println("客户端地址:" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress()); HttpRequest request = (HttpRequest) msg; URI uri = new URI(request.uri()); if ("/favicon.ico" .equals(uri.getPath())){ System.out.println("请求了favicon.ico,不做响应" ); return ; } ByteBuf content = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello,客户端" , StandardCharsets.UTF_8); FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, content); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain;charset=utf-8" ); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, content.readableBytes()); ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(response); } } }
Netty核心模块组件
Bootstrap、ServerBootstrap
一个Netty应用通常由一个Bootstrap开始,主要作用是配置整个Netty程序,串联各个组件,Netty中Bootstrap类是客户端程序的启动引导类,ServerBootstrap是服务端启动引导类
常用方法
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup):用于服务器端,用来设置两个EventLoopGroup(bossGroup和workerGroup)public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup group):用于客户端,用来设置一个EventLoopGrouppublic B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass):用来设置一个服务器端的通道实现public <T> B option(ChannelOption<T> option, T value):用来给ServerChannel添加配置public <T> ServerBootstrap childOption(ChannelOption<T> childOption, T value):用来给接收到的通道添加配置public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler):用来设置业务处理类(自定义Handler),对应的workerGroupfinal ChannelHandler handler():该Handler对应bossGrouppublic ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort):用于服务器端,用来设置占用的端口号public ChannelFuture connect(String inetHost, int inetPort):用户客户端,用来连接服务器端
Future和ChannelFuture
Netty中所有的IO操作都是异步的,不能立刻得到消息是否被正确处理,但可以过一会等它执行完成或直接注册一个监听,具体的实现就是通过Future和ChannelFuture,它们可以注册一个监听,当操作执行成功或失败时监听就会自动触发注册的监听事件
常用方法
Channel channel():返回当前正在进行I/O操作的通道ChannelFuture sync():等待异步操作执行完毕(将异步变同步)
Channel
Netty网络通信的组件,能够用于执行网络I/O操作
通过Channel可获得当前网络连接的通道的状态
通过Channel可获得网络连接的配置参数(如接收缓冲区大小)
Channel提供异步的网络I/O操作(如建立连接、读写、绑定端口),异步调用意味着任何I/O调用都将立即返回,并且不保证在调用结束时所请求的I/O操作已完成
调用立即返回一个ChannelFuture实例,通过注册监听器到ChannelFuture上,可以在I/O操作成功、失败或取消时回调通知调用方
支持关联I/O操作与对应的处理程序
不同协议、不同的阻塞类型的连接都有不同的Channel类型与之对应,常用的Channel类型:
NioSocketChannel:异步的客户端TCP Socket连接NioServerSocketChannel:异步的服务器端TCP Socket连接NioDatagramChannel:异步的UDP连接NioSctpChannel:异步的客户端Sctp连接NioSctpServerChannel:异步的Sctp服务器端连接
Selector
Netty基于Selector对象实现I/O多路复用,通过Selector一个线程可以监听多个连接的Channel事件
当向一个Selector中注册Channel后,Selector内部的机制就可以自动不断地查询(Select)这些注册的Channel是否有已就绪的I/O事件,这样程序就可以简单地使用一个线程高效管理多个Channel
ChannelHandler及其实现类
ChannelHandler是一个接口,处理I/O事件或拦截I/O操作,并将其转发到其ChannelPipeline(业务处理链)中的下一个处理程序
ChannelHandler本身并没有提供很多方法,因为这个接口有许多的方法需要实现,方便使用期间可以继承它的子类
ChannelHandler
ChannelInboundHandler用于处理入站I/O事件
ChannelOutboundHandler用于处理出站I/O操作
可能需要重写的方法
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx):通道就绪事件public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg):通道读取数据事件public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx):通道数据读取完毕事件public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause):通道发生异常事件
Pipeline和ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline是一个Handler的集合,负责处理和拦截inbound或者outbound的事件和操作,相当于一个贯穿Netty的链。(也可以理解成ChannelPipeline是保存ChannelHandler的List,用于处理或拦截Channel的入站事件和出站操作)
ChannelPipeline实现了一种高级形式的拦截过滤器模式,使用户可以完全控制事件的处理方式,以及Channel中各个ChannelHandler如何相互交互
在Netty中每个Channel都有且仅有一个ChannelPipeline与之对应
Pipeline和ChannelPipeline
一个Channel包含了一个ChannelPipeline,而ChannelPipeline中又维护了一个由ChannelHandlerContext组成的双向链表,并且每个ChannelHandlerContext中又关联着一个ChannelHandler
入站事件和出站事件在一个双向链表中,入站事件会从链表head往后传递 到最后一个入站的handler,出站事件会从链表tail往前传递 到最前一个出站handler,两种类型的handler互不干扰
常用方法
ChannelPipeline addLast(ChannelHandler... handlers):将一个业务处理类(handler)添加到最后一个位置ChannelPipeline addFirst(ChannelHandler... handlers):将一个业务处理类(handler)添加到第一个位置
ChannelHandlerContext
保存Channel相关的所有上下文信息,同时关联一个ChannelHandler对象
ChannelHandlerContext中包含一个具体的事件处理器ChannelHandler,同时ChannelHandlerContext中也绑定了对应的pipeline和channel的信息,方便对ChannelHandler进行调用
常用方法
ChannelFuture close():关闭通道ChannelOutboundInvoker flush();:刷新ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg):将数据写到ChannelPipeline当前ChannelHandler的下一个ChannelHandler处理
ChannelOption
Netty创建Channel实例后,一般都需要设置ChannelOption参数,如:
ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG:对应TCP/IP协议listen函数中的backlog参数,用来初始化服务器可连接队列大小 。服务端处理客户端连接请求是顺序处理的,所以同一时间只能处理一个客户端连接。多个客户端来的时候,服务端将不能处理的客户端连接请求放在队列中等待处理,backlog参数指定了队列的大小。ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE:一直保持连接活动状态
EventLoopGroup和其实现类NioEventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup是一组EventLoop的抽象,Netty为了更好的利用多核CPU资源,一般会有多个EventLoop同时工作,每个EventLoop维护着一个Selector实例
EventLoopGroup提供next接口,可以从组里面按照一定规则获取其中一个EventLoop来处理任务 。在Netty服务器编程中,一般都需要提供两个EventLoopGroup
通常一个服务端口即一个ServerSocketChannel对应一个Selector和一个EventLoop线程。BossEventLoop负责接收客户端的连接并将SocketChannel交给WorkerEventLoopGroup来进行IO处理
BossEventLoopGroup通常是一个单线程的EventLoop ,EventLoop维护着一个注册了ServerSocketChannel的Selector实例,BossEventLoop不断轮询Selector 将连接事件分离出来。通常是OP_ACCEPT 事件,然后将接收到的SocketChannel交给WorkerEventLoopGroup
WorkerEventLoopGroup会由next选择其中一个EventLoop 来将这个SocketChannel注册到其维护了Selector并对其后续的I/O事件进行处理。
常用方法
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads):构造方法public Future<?> shutdownGracefully():断开连接,关闭线程
Unpooled类
Netty提供的一个专门用来操作缓冲区(即Netty的数据容器)的工具类
ByteBuf中,不需要使用flip进行反转,底层维护了readIndex和writeIndex,通过readIndex、writeIndex和capacity将buffer分成三个区域
常用方法
public static ByteBuf copiedBuffer(CharSequence string, Charset charset):通过给定的数据和字符编码返回一个ByteBuf对象(类似于NIO中的ByteBuffer,但有区别)
群聊案例
服务端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class GroupChatServer private int port; public GroupChatServer (int port) this .port = port; } public void run () throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8 ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception ch.pipeline().addLast("decoder" , new StringDecoder()) .addLast("encoder" , new StringEncoder()) .addLast(new GroupChatServerHandler()); } }); System.out.println("服务器启动" ); ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync(); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException new GroupChatServer(9999 ).run(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 public class GroupChatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler <String > private static ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE); DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" ); @Override public void handlerAdded (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception Channel channel = ctx.channel(); channelGroup.writeAndFlush(LocalDateTime.now().format(formatter) + ":" + "[客户端]" + channel.remoteAddress() + "加入聊天!\r\n" ); channelGroup.add(channel); } @Override public void handlerRemoved (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception Channel channel = ctx.channel(); channelGroup.writeAndFlush(LocalDateTime.now().format(formatter) + ":" + "[客户端]" + channel.remoteAddress() + "离开了!\r\n" ); } @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now().format(formatter) + ":" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "已经上线~" ); } @Override public void channelInactive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now().format(formatter) + ":" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "已经离线~" ); } @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception Channel channel = ctx.channel(); channelGroup.forEach(ch -> { if (ch != channel) { ch.writeAndFlush(LocalDateTime.now().format(formatter) + ":" + "[客户]" + channel.remoteAddress() + ":" + msg + "\r\n" ); } else { ch.writeAndFlush(LocalDateTime.now().format(formatter) + ":" + "[自己]" + channel.remoteAddress() + ":" + msg + "\r\n" ); } }); } @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception ctx.close(); } }
客户端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class GroupChatClient private final String host; private final int port; public GroupChatClient (String host, int port) this .host = host; this .port = port; } public void run () throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception ch.pipeline().addLast("decoder" , new StringDecoder()) .addLast("encoder" , new StringEncoder()) .addLast(new GroupChatClientHandler()); } }); ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync(); Channel channel = future.channel(); System.out.println("-------" + channel.localAddress() + "-------" ); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (scanner.hasNextLine()){ String msg = scanner.nextLine(); channel.writeAndFlush(msg + "\r\n" ); } future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully(); } } public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException new GroupChatClient("127.0.0.1" , 9999 ).run(); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class GroupChatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler <String > @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception System.out.println(msg.trim()); } }
心跳检测机制
心跳机制是定时发送一个自定义的结构体(心跳包),让对方知道自己还活着,以确保连接的有效性的机制。
案例
服务器通过IdleStateHandler根据读写情况定时发送心跳检测包来判断客户端是否存活
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public class Server public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8 ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(3 , 5 , 7 , TimeUnit.SECONDS)) .addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void userEventTriggered (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent){ IdleStateEvent idleStateEvent = (IdleStateEvent) evt; String eventType = null ; switch (idleStateEvent.state()){ case READER_IDLE: eventType = "读空闲" ; break ; case WRITER_IDLE: eventType = "写空闲" ; break ; case ALL_IDLE: eventType = "读写空闲" ; break ; default : break ; } System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "--超时事件:" + eventType); } } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9999 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
WebSocket长连接
HTTP协议是无状态的,浏览器和服务器间请求响应一次,下次会重新创建连接
WebSocket是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通信的协议,实现了浏览器与服务器全双工通信,能更好的节省服务器资源和带宽并达到实时通讯的目的
WebSocket可以改变Http协议多次请求的约束,实现长连接,使得服务器可以发送消息给浏览器
客户端和浏览器也可以相互感知
案例
需求:
实现基于WebSocket的长连接的全双工交互
浏览器可以知道服务器关闭,服务器也能知道浏览器断开连接
浏览器可以向服务器发送消息,服务器也能向浏览器发送消息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 public class MyServer public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8 ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec(), new ChunkedWriteHandler(), new HttpObjectAggregator(8192 ), new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/xxx" ), new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame>() { @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception System.out.println("服务器收到消息" + msg.text()); ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("服务器时间:" + LocalDateTime.now() + " 消息:" + msg.text())); } @Override public void handlerAdded (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception System.out.println("已连接:" + ctx.channel().id().asLongText()); } @Override public void handlerRemoved (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception System.out.println("已断开:" + ctx.channel().id().asLongText()); } @Override public void exceptionCaught (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception System.out.println("异常发生:" + cause.getMessage()); ctx.close(); } } ); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9999 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > </head > <body > <script > let socket; if (window .WebSocket) { socket = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:9999/xxx" ) socket.onmessage = function (ev ) let rt = document .getElementById("responseText" ); rt.value = rt.value + '\n' + ev.data; } socket.onopen = function (ev ) let rt = document .getElementById("responseText" ); rt.value = rt.value + "连接已开启..." ; } socket.onclose = function (ev ) let rt = document .getElementById("responseText" ); rt.value = rt.value + "连接已关闭..." ; } function send (msg ) if (window .WebSocket) { if (socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN){ socket.send(msg); }else { alert("连接未开启" ) } } } } else { alert("浏览器不支持WebSocket" ) } </script > <form onsubmit ="return false" > <textarea name ="message" style ="height: 300px; width: 300px" > </textarea > <input type ="button" value ="发送" onclick ="send(this.form.message.value)" > <textarea id ="responseText" style ="height: 300px; width: 300px" > </textarea > <input type ="button" value ="清空" onclick ="document.getElementById('responseText').value=''" > </form > </body > </html >
Google Protobuf
Netty的编码解码机制
Netty本身提供了一些codec(编解码器),如:
编码器:
StringEncoder:对字符串数据进行编码
ObjectEncoder:对Java对象进行编码
...
解码器
StringDecoder:对字符串进行解码
ObjectDecoder:对Java对象进行解码
...
Netty本身自带的ObjectDecoder和ObjectEncoder可以用来实现POJO对象或各种业务对象的编码和解码,底层使用的仍是Java序列化技术,而Java序列化技术本身效率就不高,存在如下问题:
无法跨语言
序列化后体积太大,是二进制编码的5倍多
序列化性能太低
Protobuf
Protobuf 是Google发布的开源项目,全称是Google Protocal Buffers,是一种轻便高效的结构化数据存储格式,可以用于结构化数据串行化,或者说序列化。很适合做数据存储或RPC数据交换格式。目前很多公司就在从http+json向tcp+protobuf转型Protobuf是以message的方式来管理数据的
支持跨平台、跨语言
高性能、高可靠性
使用protobuf编译器能自动生成代码,Protobuf是将类的定义使用.proto文件进行描述,然后通过protoc.ext编译器根据.proto自动生成.java文件
案例
需求:
客户端随机发送Student对象或Worker对象给服务器(通过Protobuf编码)
服务器接收对象后显示对应的信息(通过Protobuf解码)
流程:
引入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > com.google.protobuf</groupId > <artifactId > protobuf-java</artifactId > <version > 3.21.7</version > </dependency >
编写proto文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 syntax = "proto3" ; option optimize_for = SPEED; option java_package = "com.zephon.netty_learn.protobuf" ; option java_outer_classname = "MyDataInfo" ; message MyMessage{ enum DataType StudentType=0 ; WorkerType=1 ; } DataType data_type=1 ; oneof dataBody{ Student student=2 ; Worker worker=3 ; } } message Student{ int32 id = 1 ; string name = 2 ; } message Worker{ string name=1 ; int32 age=2 ; }
编译proto文件,通过maven配置插件,然后使用maven编译
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 <build> <extensions> <extension> <groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId> <artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>1.4 .1 .Final</version> </extension> </extensions> <plugins> <!-- Protobuf插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>0.5 .1 </version> <configuration> <protoSourceRoot>${project.basedir}/src/main/proto</protoSourceRoot> <protocArtifact> com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.21 .7 :exe:${os.detected.classifier} </protocArtifact> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>compile</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
编写服务器端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class ProServer public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8 ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception ch.pipeline().addLast( new ProtobufDecoder(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.getDefaultInstance()), new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MyDataInfo.MyMessage>() { @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MyDataInfo.MyMessage msg) throws Exception MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType dataType = msg.getDataType(); if (dataType == MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.StudentType) { MyDataInfo.Student student = msg.getStudent(); System.out.println("客户端发送Student: id=" + student.getId() + ", name=" + student.getName()); } else if (dataType == MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.WorkerType){ MyDataInfo.Worker worker = msg.getWorker(); System.out.println("客户端发送Worker: name=" + worker.getName() + ", age=" + worker.getAge()); } else { System.out.println("传输类型不正确" ); } } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
编写客户端
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public class ProClient public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception socketChannel.pipeline().addLast( new ProtobufEncoder(), new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception int r = new Random().nextInt(3 ); MyDataInfo.MyMessage myMessage = null ; if (0 == r) { myMessage = MyDataInfo.MyMessage.newBuilder() .setDataType(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.StudentType) .setStudent(MyDataInfo.Student.newBuilder().setId(3 ).setName("张三" ).build()).build(); } else { myMessage = MyDataInfo.MyMessage.newBuilder() .setDataType(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.WorkerType) .setWorker(MyDataInfo.Worker.newBuilder().setName("李四" ).setAge(20 ).build()).build(); } System.out.println(myMessage); ctx.writeAndFlush(myMessage); } }); } }); System.out.println("客户端已准备好" ); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1" , 8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
Netty编解码器和Handler的调用机制
入站与出站
Netty的主要组件有:Channel、EventLoop、ChannelFuture、ChannelHandler和ChannelPipe等
ChannelHandler充当了处理入站和出站数据的应用程序逻辑的容器。如:实现ChannelInboundHandler接口(或ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter),就可以接收入站事件和数据,这些数据会被业务逻辑处理。当要给客户端发送响应时,也可以从ChannelInboundHandler冲刷数据。业务逻辑通常写在一个或多个ChannelInboundHandler中。ChannelOutboundHandler原理一样,只不过它是用来处理出站数据的
ChannelPipeline提供了ChannelHandler链的容器,以客户端应用程序为例,如果事件运动方向是从客户端到服务端,则是出站,反之为入站
编码与解码
当Netty发送或接收一个消息时,就会发生一次数据转换,入站消息会被解码:从字节转换为另一种格式(如Java对象),如果是出站消息,就会被编码成字节
Netty提供的一系列实用的编解码器,都实现了ChannelInboundHandler或ChannelOutboudHandler接口。在这些类中,channelRead方法已经被重写了,以入站为例,对于每个从入站Channel读取的消息,这个方法会被调用,随后将调用由解码器所提供的decode()方法进行解码,并将解码的字节转发给ChannelPipeline的下一个ChannelInboundHandler
自定义编解码器案例
客户端发送long类型数据到服务器
服务器接收long类型数据并显示
客户端与编码器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class Client public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception socketChannel.pipeline().addLast( new MessageToByteEncoder<Long>() { @Override protected void encode (ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Long aLong, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception System.out.println("encode被调用" ); System.out.println("msg=" + aLong); byteBuf.writeLong(aLong); } }, new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception ctx.writeAndFlush(123456L ); } }); } }); System.out.println("客户端已准备好" ); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1" , 8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
服务端与解码器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class Server public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8 ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception ch.pipeline().addLast( new ByteToMessageDecoder() { @Override protected void decode (ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf, List<Object> list) throws Exception while (byteBuf.readableBytes() >= 8 ) { list.add(byteBuf.readLong()); } } }, new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Long>() { @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Long msg) throws Exception System.out.println("从客户端读取long:" + msg); } } ); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
Netty其它常用编解码器
public abstract class ReplayingDecoder<S> extends ByteToMessageDecoder:ReplayingDecoder扩展了ByteToMessageDecoder类,使用这个类,不需要调用readableBytes()方法,参数S指定了用户状态管理的类型,其中Void代表不需要状态管理
存在局限性:
并不是所有的ByteBuf操作都支持,如果调用了不被支持的方法,就会抛出异常
在某些情况下可能稍慢于ByteToMessageDecoder,如网络缓慢并且消息格式复杂时,消息会被拆成多个碎片,速度变慢
public class LineBasedFrameDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder:这个类在Netty内部也有使用,使用行尾控制字符(\r)作为分割符来解析数据public class DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder:使用自定义的特殊字符作为消息的分隔符public abstract class HttpObjectDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder:一个HTTP数据的解码器public class LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder:通过指定长度来标识整包消息,这样就可以自动处理粘包和半包消息...
TCP粘包和拆包及解决方案
TCP是面向连接、面向流的,提供高可靠性服务。收发两端(客户端和服务器端)都要有一一成对的Socket,因此,发送端为了将多个发送给接收端的包更有效的发送,使用了优化算法(Nagle算法),将多次间隔较小且数据量小的数据,合并成一个大的数据块,然后进行封包。这样虽然提高了效率,但接收端就很难分辨出完整的数据包,因为面向流的通信是无消息保护边界的
由于TCP无消息保护边界,需要在接收端处理消息边界问题,也就是所谓的粘包、拆包问题
具体地,假设客户端发送了两个数据包D1和D2,则:
如果服务端分两次读取两个独立的数据包,分别是D1和D2,则没有粘包和拆包
如果服务端一次接收到了两个数据包,D1和D2粘合在一起,则称为TCP粘包
如果服务端分两次读取到数据包,第一次读取到了完成的D1和部分D2,第二次读取到了D2包的剩余内容,则称为TCP拆包
如果服务端分两次读取到了数据包,第一次读取到了D1包的部分内容,第干净读取到了D1的剩余部分同窗和完成的D2包
TCP粘包和拆包案例
服务器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class Server public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8 ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception ch.pipeline().addLast( new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { private int count; @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception byte [] buffer = new byte [msg.readableBytes()]; msg.readBytes(buffer); String s = new String(buffer, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); System.out.println("服务器端接收到数据:" + s); System.out.println("服务器端接收到消息量:" + ++count); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } } ); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
客户端:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class Client public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) socketChannel.pipeline().addLast( new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){ ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(" hello ,server" + i, StandardCharsets.UTF_8); ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); } } @Override public void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) byte [] bytes = new byte [msg.readableBytes()]; msg.readBytes(bytes); System.out.println(new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } }); } }); System.out.println("客户端已准备好" ); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1" , 8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
输出:
服务器端接收到数据: hello ,server0 服务器端接收到消息量:1 服务器端接收到数据: hello ,server1 服务器端接收到消息量:2 服务器端接收到数据: hello ,server2 hello ,server3 服务器端接收到消息量:3 服务器端接收到数据: hello ,server4 hello ,server5 hello ,server6 服务器端接收到消息量:4 服务器端接收到数据: hello ,server7 hello ,server8 hello ,server9 服务器端接收到消息量:5
解决
使用自定义协议+编解码器来解决
关键就是要解决服务器端每次读取数据长度的问题
自定义协议包:
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Data @AllArgsConstructer public class MessageProtocol private int len; private byte [] content; }
自定义编码器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class MyMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder <MessageProtocol > @Override protected void encode (ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, MessageProtocol messageProtocol, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception System.out.println("调用encode方法" ); byteBuf.writeInt(messageProtocol.getLen()); byteBuf.writeBytes(messageProtocol.getContent()); } }
自定义解码器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class MyMessageDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder @Override protected void decode (ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf, List<Object> list) throws Exception System.out.println("调用decode" ); int len = byteBuf.readInt(); byte [] content = new byte [len]; byteBuf.readBytes(content); MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol(len, content); list.add(messageProtocol); } }
服务端:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public class Server public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1 ); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(8 ); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128 ) .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true ) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel ch) throws Exception ch.pipeline().addLast( new MyMessageEncoder(), new MyMessageDecoder(), new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocol>() { private int count; @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg) throws Exception int len = msg.getLen(); byte [] content = msg.getContent(); System.out.println("服务端接收到信息:" ); System.out.println("长度=" + len); System.out.println("内容=" + new String(content, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); System.out.println("服务器接收到消息次数: " + ++count); byte [] response = UUID.randomUUID().toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); ctx.writeAndFlush(new MessageProtocol(response.length, response)); } } ); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
客户端:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public class Client public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel (SocketChannel socketChannel) socketChannel.pipeline().addLast( new MyMessageEncoder(), new MyMessageDecoder(), new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocol>() { @Override public void channelActive (ChannelHandlerContext ctx) for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) { byte [] content = "醉卧沙场君莫笑,古来征战几人回" .getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol(content.length, content); ctx.writeAndFlush(messageProtocol); } } @Override protected void channelRead0 (ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg) throws Exception System.out.println("客户端收到:" ); System.out.println(new String(msg.getContent(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } }); } }); System.out.println("客户端已准备好" ); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1" , 8888 ).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
输出:
调用decode 服务端接收到信息: 长度=45 内容=醉卧沙场君莫笑,古来征战几人回 服务器接收到消息次数: 1 调用encode方法 调用decode 服务端接收到信息: 长度=45 内容=醉卧沙场君莫笑,古来征战几人回 服务器接收到消息次数: 2 调用encode方法 调用decode 服务端接收到信息: 长度=45 内容=醉卧沙场君莫笑,古来征战几人回 服务器接收到消息次数: 3 调用encode方法 调用decode 服务端接收到信息: 长度=45 内容=醉卧沙场君莫笑,古来征战几人回 服务器接收到消息次数: 4 调用encode方法 调用decode 服务端接收到信息: 长度=45 内容=醉卧沙场君莫笑,古来征战几人回 服务器接收到消息次数: 5 调用encode方法